FUNCTIONAL MEDICINE
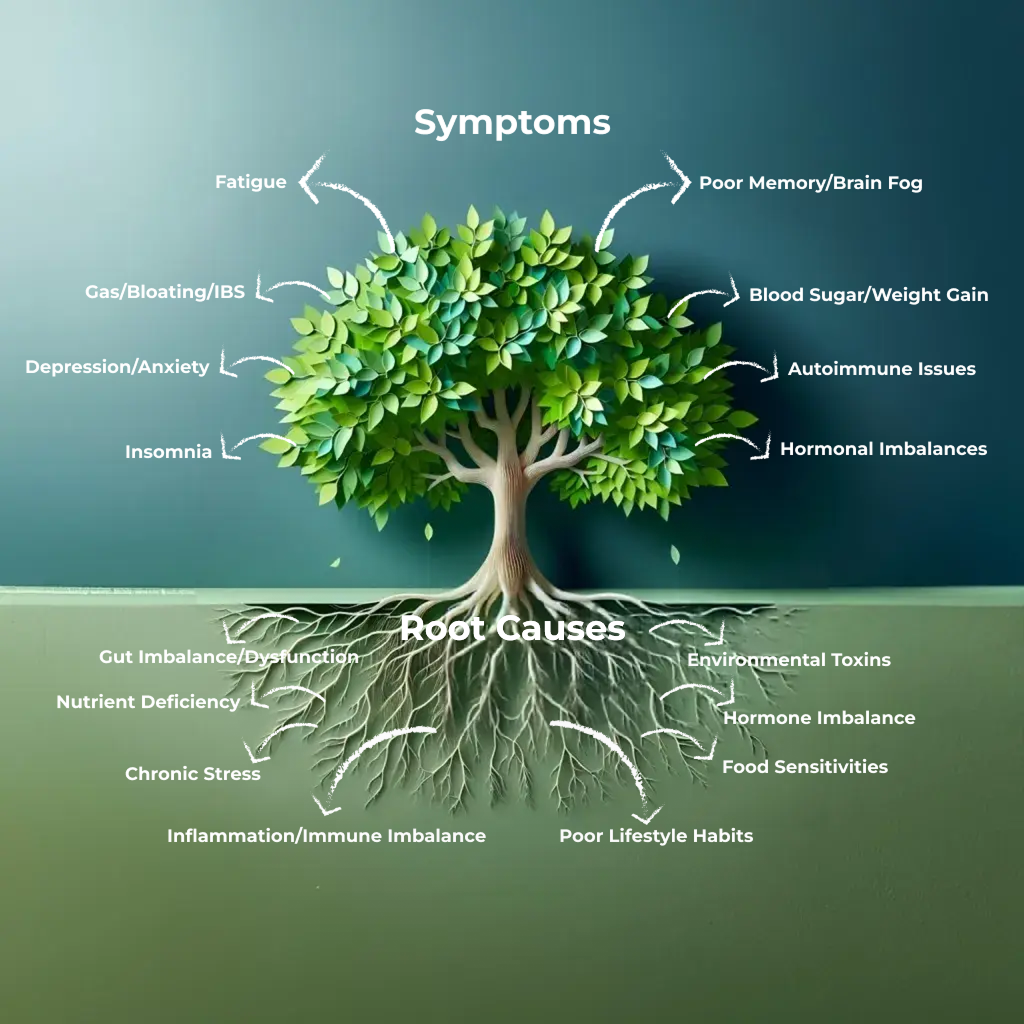
Functional medicine focuses on addressing the root causes of health issues
and restoring health and well-being.
The aim of Functional medicine is to prevent and treat chronic health
problems by addressing the underlying imbalances in the body
Inflammation is a protective mechanism that helps to remove harmful
substances, repair damaged tissue, and prevent infection. However,
chronic inflammation, which lasts for an extended period of time, can be
harmful and contribute to the development of various diseases.
Key aspects of functional medicine:

Root Cause:
Unlike conventional medicine that solely treats symptoms, functional medicine seeks to identify and address the underlying causes of health issues.

Holistic:
It considers the entire person including their physical, emotional, and environmental symptoms , rather than just focusing on a single organ or
disease.

Personalized:
Functional medicine practitioners develop individualized plans tailored to each patient’s unique needs and circumstances.

Collaboration:
It empowers the patient to actively participate in their health journey

Systems Based:
It views the body as a network of interconnected systems, and health
problems are seen as disturbances within these systems.

Prevention:
Functional medicine can be helpful for managing a variety of conditions, including:
- Chronic diseases (e.g., diabetes, heart disease)
- Digestive disorders (e.g., SIBO, IBS, Crohn's disease)
- Autoimmune diseases (e.g., psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus)
- Hormonal imbalances (e.g., thyroid disorders, PMS.menopause)
- Mental health conditions (e.g., depression, anxiety, ADHD)
- Other conditions (e.g., allergies, chronic pain)

