Inflammation is a protective mechanism that helps to remove harmful substances, repair damaged tissue, and prevent infection. However, chronic inflammation, which lasts for an extended period of time, can be
harmful and contribute to the development of various diseases.
Causes

1. Diet and Nutrition:
- Inflammatory Foods: Diets high in processed foods, sugar, unhealthy fats, and refined carbohydrates can trigger and exacerbate inflammation.
- Food Sensitivities: Undetected food sensitivities (e.g., gluten, dairy, soy) can cause chronic, low-grade inflammation in susceptible individuals.
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Inadequate intake or absorption of key nutrients, like omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and certain vitamins, can impair the body's ability to regulate inflammation.
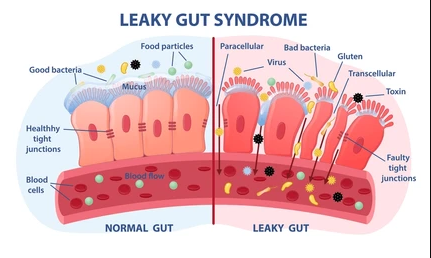
2. Gut Health:
- Leaky Gut (Increased Intestinal Permeability): A compromised gut lining allows undigested food particles, toxins, and bacteria to leak into the bloodstream, triggering an inflammatory immune response.
- Dysbiosis (Gut Microbiome Imbalance): An imbalance of beneficial and harmful bacteria in the gut can disrupt immune function and contribute to inflammation.

3. Stress and Emotional Well-being:
- Chronic Stress: Prolonged stress can elevate cortisol levels, which, in turn, can fuel inflammation.
- Sleep Deprivation: Poor sleep quality and insufficient sleep can disrupt circadian rhythms and increase inflammation.

4. Environmental Toxins:
- Exposure to Toxins: Environmental toxins, such as pollutants, pesticides, heavy metals, and chemicals found in everyday products, can burden the body's detoxification pathways and trigger inflammation.

5. Lifestyle Factors:
- Lack of Exercise: Physical inactivity can contribute to inflammation, while regular exercise can have anti-inflammatory effects.
- Obesity: Excess body fat, especially visceral fat, can produce inflammatory molecules.
Health Problems:
Chronic inflammation can be a root cause or a significant contributing factor
to a wide range of health problems, including:

1.Digestive Disorders:
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Conditions like Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis are characterized by chronic inflammation in the digestive tract.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Inflammation can play a the symptoms of IBS.

2.Skin Disorders:
- Conditions like psoriasis and eczema involve chronic inflammation in the skin

3. Metabolic Disorders:
- Type 2 Diabetes: Inflammation impairs insulin sensitivity and contributes to the development of insulin resistance, a hallmark of type 2 diabetes.
- Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome: Chronic low-grade inflammation, particularly in adipose tissue, is linked to obesity, metabolic syndrome, and associated conditions.

4. Mental Health Conditions
- Depression and Anxiety: Research suggests that inflammation may contribute to the development of mood disorders.

5. Autoimmune Diseases:
- Rheumatoid Arthritis, Lupus, Hashimoto's: Chronic inflammation is a central feature of autoimmune diseases, where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues.

6. Neurodegenerative Diseases:
- Alzheimer's and Parkinson's: Chronic inflammation is increasingly recognized as a factor in the development and progression of neurodegenerative diseases
7.Cardiovascular Disease:
- Atherosclerosis: Inflammation plays a key role in the development of plaque buildup in arteries, which increases the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Hypertension: Inflammation can contribute to the development and progression of high blood pressure.

8.Chronic Pain Conditions:
- Fibromyalgia and Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: Inflammation may play a role in the widespread pain and fatigue associated with these conditions

9. Certain Cancers:
- Chronic inflammation can create an environment that promotes cancer development and progression.

10. Respiratory Conditions:
- Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Inflammation in the airways is a key feature of these respiratory conditions.

